
The UN's sustainable development goal (SDG) #3, Good Health and Well-Being, involves ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all at all ages. According to the FAO report, humans currently produce more food per person than before. However, around 720 to 811 million people worldwide faced hunger in 2020. Our current food system affects groundwater resources, produces one-third of greenhouse gases, consumes land and resources, disrupts natural ecosystems, and causes biodiversity loss (FAO, 2020). Therefore the concept of the future food emerged. Generally, this concept is accompanied by start-ups in agriculture or related fields of the food and beverage industry, farming, and related industries which are about the production of alternative products, especially proteins, or new products.

Food innovation refers to the development of new food, products, and services that significantly contribute to industry productivity and market choices. Although producing food from electricity and CO2 may sound like science fiction movies, the truth is that it is possible! It is possible to convert CO2 into edible fat and protein with electricity on a laboratory scale. Food innovation is to improve the life of the consumer and the efficiency of the food business process, which must reduce food waste and deal with climate change, inside and outside the food chain.
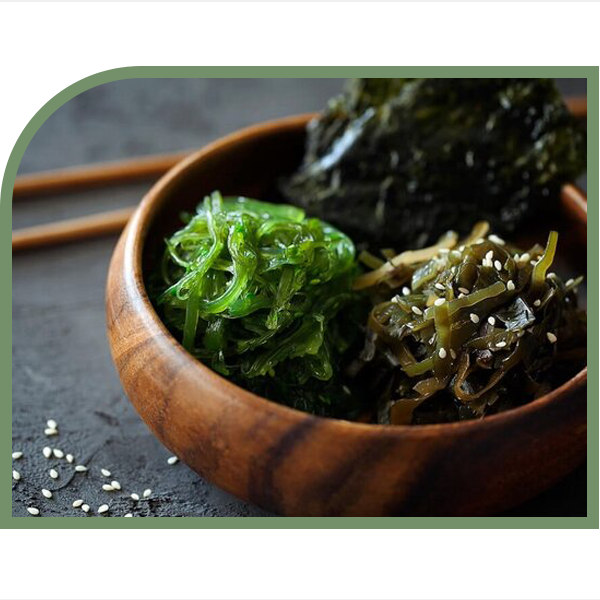
Future food is a type of food that our ability to produce in mass quantities is rapidly advancing due to technological development. Based on data there are nine future food are as follows: terrestrial foods (farmed meat, mycoprotein, black soldier fly larvae, housefly larvae, roundworm larvae) and aquatic food (seaweeds such as chlorella, spirulina ), sugary brown algae, and sea shell (mussels).

The goals of future food are the production of food with high nutritional value, low environmental footprint, and low carbon emissions, which is in line with the sustainability agenda provided by the United Nations considering the sustainable future of the planet and climate change. Therefore, future food start-ups in the field of agriculture have unveiled modified seeds and organic and high-yield cultivation methods. The manufacturing industry has presented new packaging and producing food methods like food storage devices that are sustainable and with low environmental footprint. Additionally, restaurants have presented organic food preparation methods and new flavors in line with the changing human taste. Here are are some examples: urban farms, innovative cultivation methods such as hydroponics, community gardens, sustainable packaging, and sustainable food products.
To conclude, there are currently six emerging trends shaping the future of food as follows:
1. Made in the laboratory.
2. Less natural resources consumption
3. Justice in access and distribution of food people
4. High nutritional value
5. Less waste
6. Changing global taste